Reverse Osmosis is a membrane filtration technology that works by forcing water under pressure through the very tiny pores of a semi-permeable membrane to produce highly purified, great-tasting water.
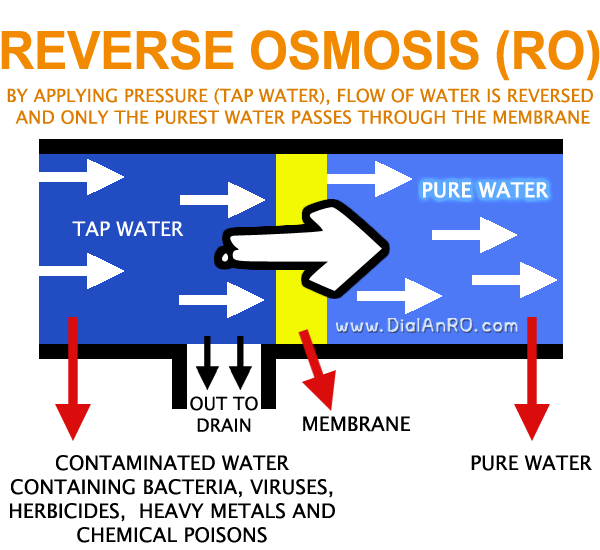
Unlike Osmosis, Reverse Osmosis {RO} is a process where the flow of the water is reversed by applying external pressure to the concentrated (polluted) side.
The water is forced through a synthetic semi-permeable membrane by applying strong pressure, that allows only fine water (H2O) molecules to pass through it.
In other words, when pressure is applied to the contaminated water, only the purest water passes through the membrane and rest is left behind and is drained out.
All contaminants such as bacteria, viruses, herbicides, heavy metals and chemical poisons are removed.
With added special features, pure water is then collected in a container and dirty water with impurities is discharged separately.
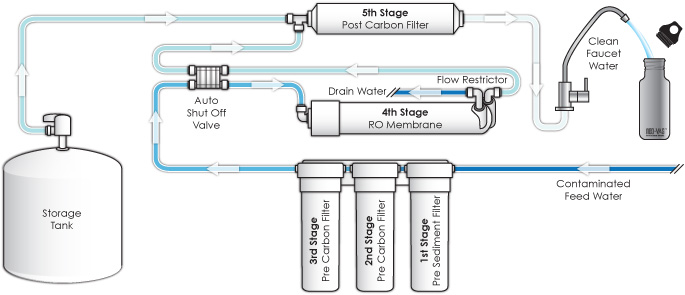
Reverse Osmosis is an advanced water purification method that was initially developed by the U.S. Navy to produce drinking water from sea water for submarine crews.
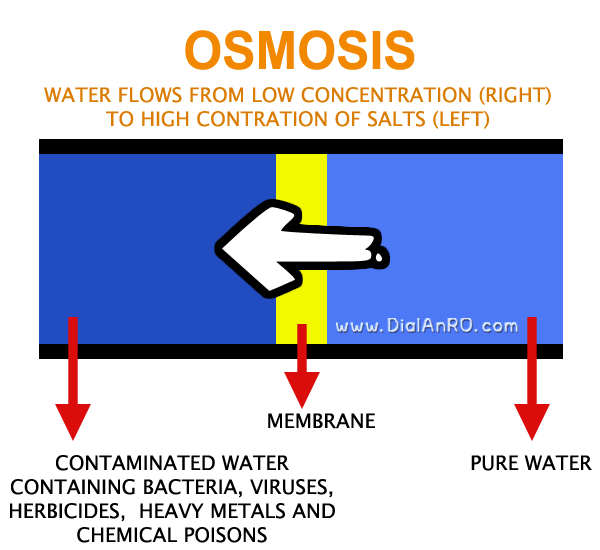
Osmosis Process
To better understand Reverse Osmosis Process, it would help to first know what is Osmosis Process.
When a semipermeable membrane (a very thin sheet with extremely tiny holes) is placed between less salty water AND water with more salts (saline water), water molecules automatically move & flow from less concentrated solution (less salty) to stronger saline solution (more salty). This process is called Osmosis.
If the above process is reversed by applying external pressure, it becomes Reverse Osmosis Process.